
Peru reveals replica of face of ancient female ruler
July 5, 2017 - Reuters
"Its relevance is really incalculable," del Solar said of the oval-shaped face with high cheekbones on display under a golden crown. "We can now show the world her face, a face that Peruvians see ourselves in."
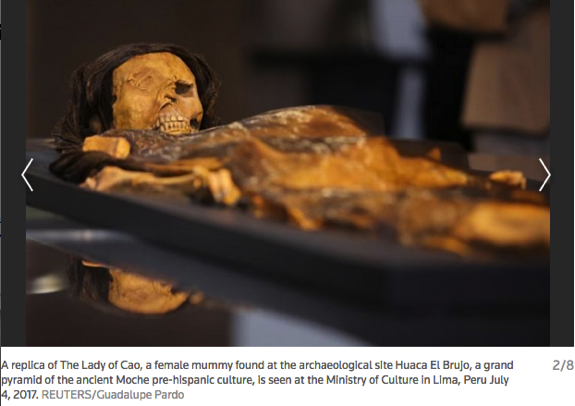

The discovery of the Lady of Cao's mummified remains in 2005 shattered the belief that the ancient Moche society, which occupied the Chicama Valley from about 100 to 700 A.D., was patriarchal. Several Moche female mummies have been found since in graves with objects denoting a high political and religious standing.
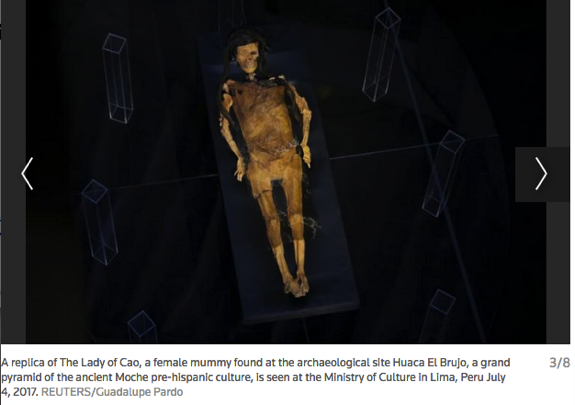
Archaeologists believe the Lady of Cao died due to complications of childbirth but otherwise lived a healthy life.
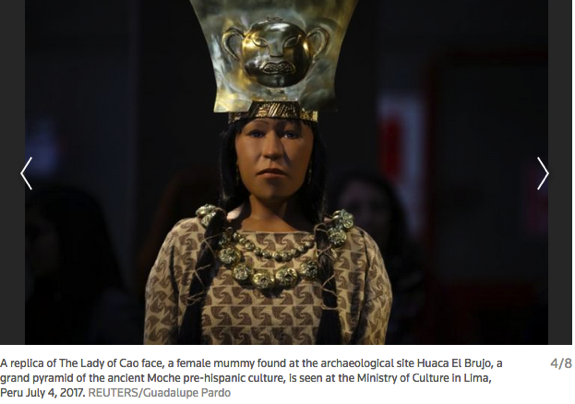

Her arms and legs were covered with tattoos of snakes, spiders and other supernatural motifs. Discovered near her funerary bundle was a strangled adolescent, who might have been a sacrifice to guide her into the afterlife, according to the museum at the El Brujo archaeological site where she was found.

The Lady of Cao is a reminder of the complex societies that thrived in what is now Peru long before the Inca empire dominated the Andes or Europeans arrived in the Americas.

The Moche built irrigation canals to grow crops in the desert and were known for their ceramics and goldwork that have been looted from their gravesites.

The replica of the Lady of Cao, a collaboration that included archaeologists, the Wiese Foundation and global imaging company FARO Technologies Inc, will be displayed in Peru's culture ministry in the capital Lima through July 16. It will later be shown at the museum at El Brujo.

(Reporting by Reuters TV and Mitra Taj; Editing by Matthew Lewis)
